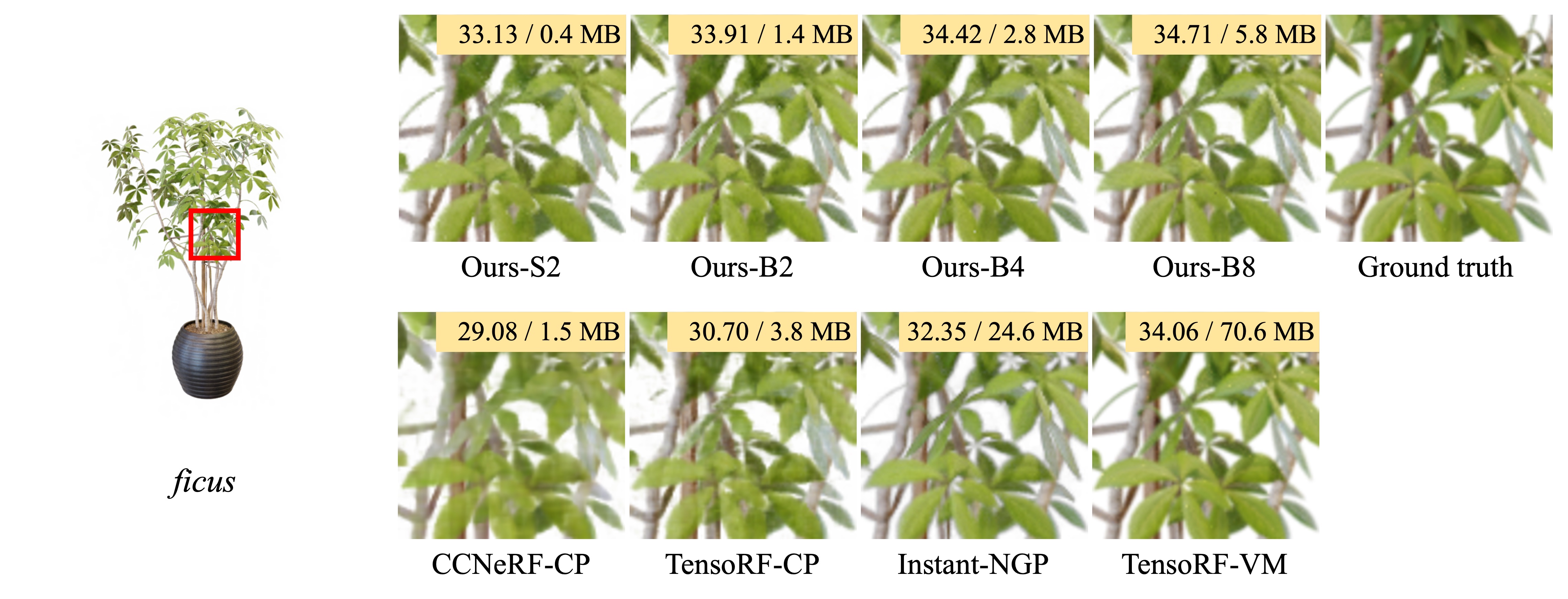
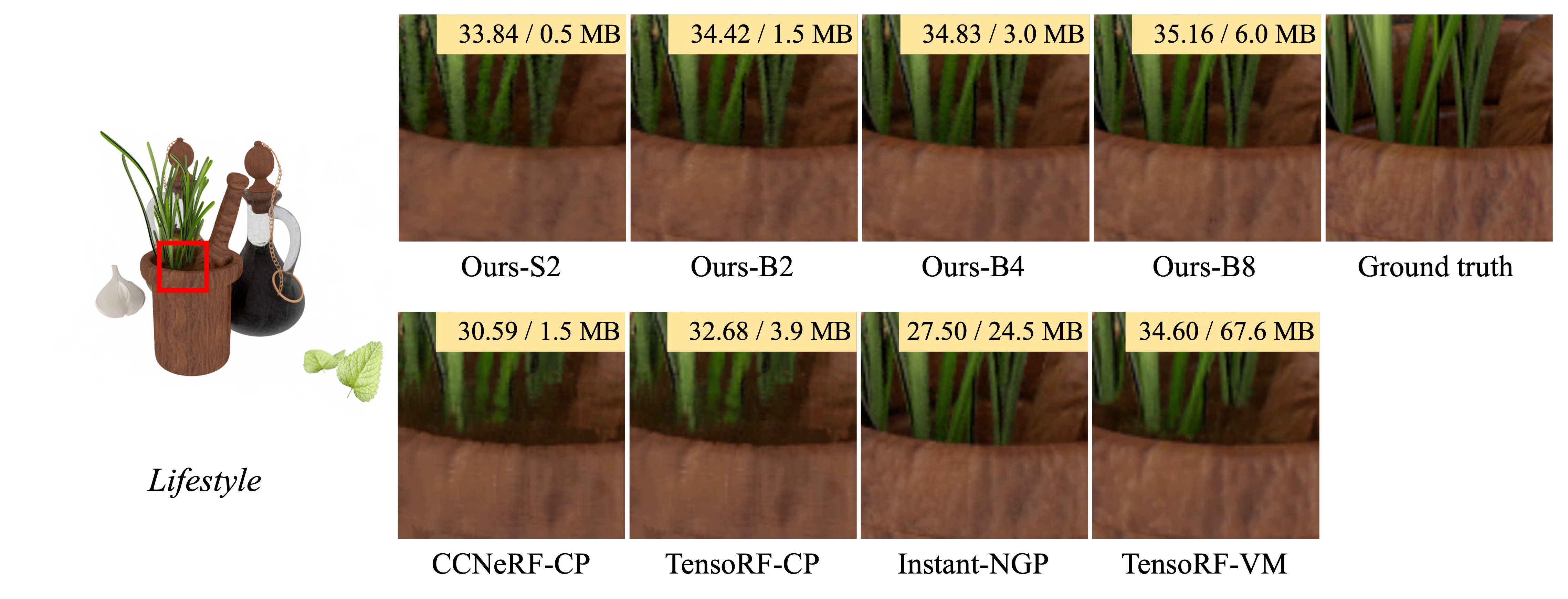
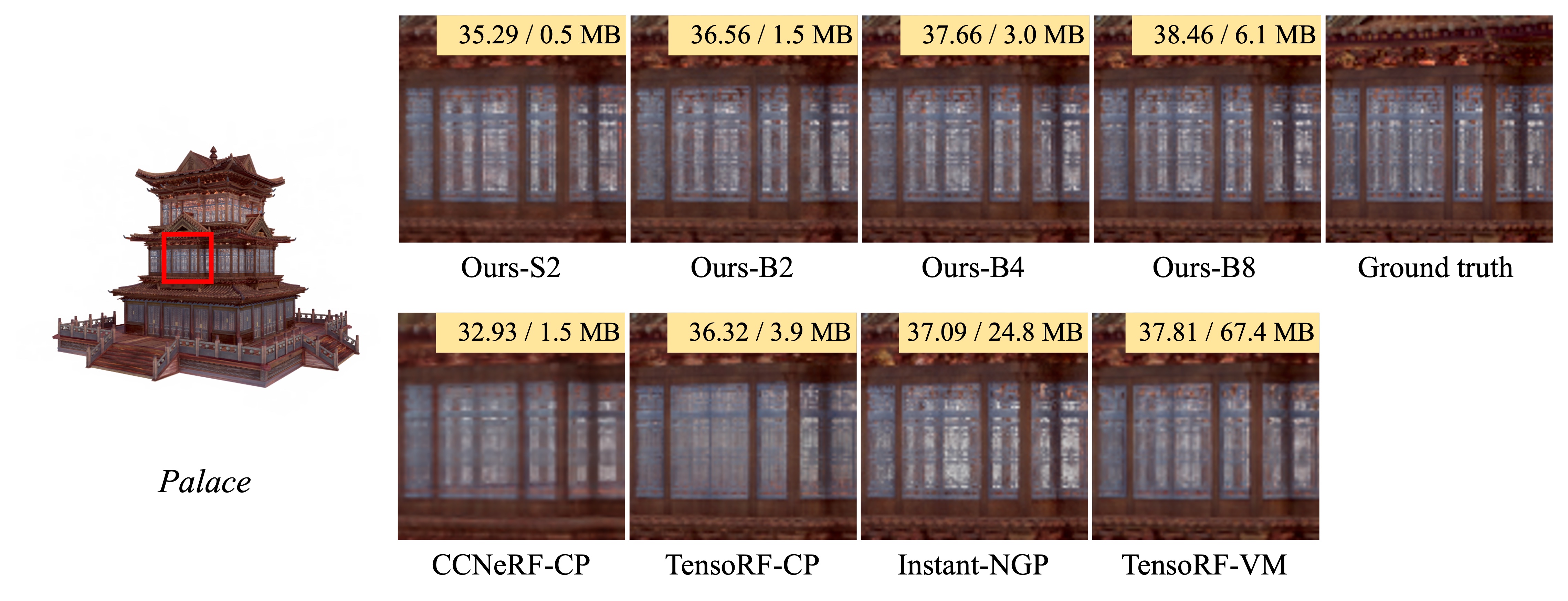
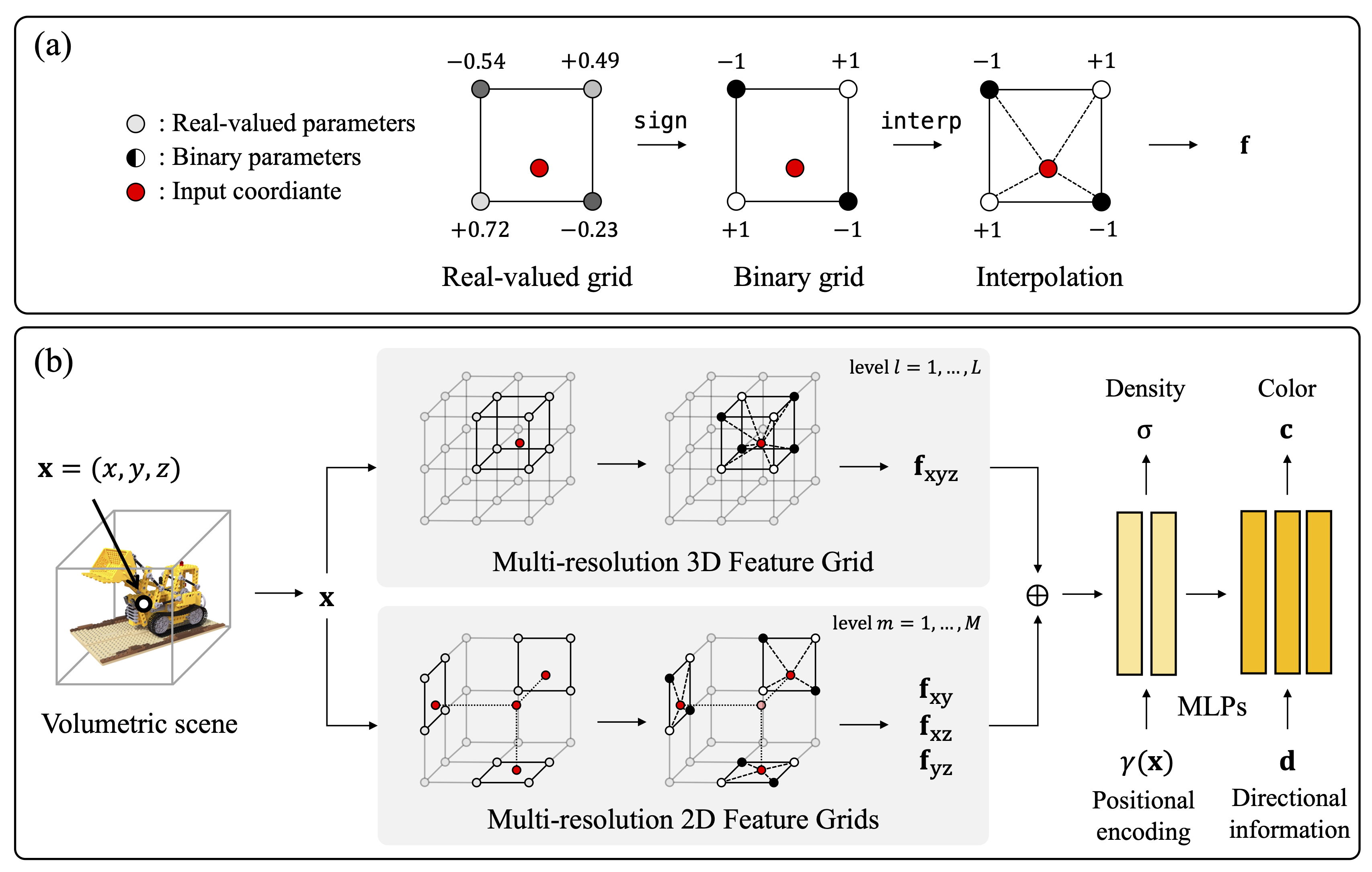
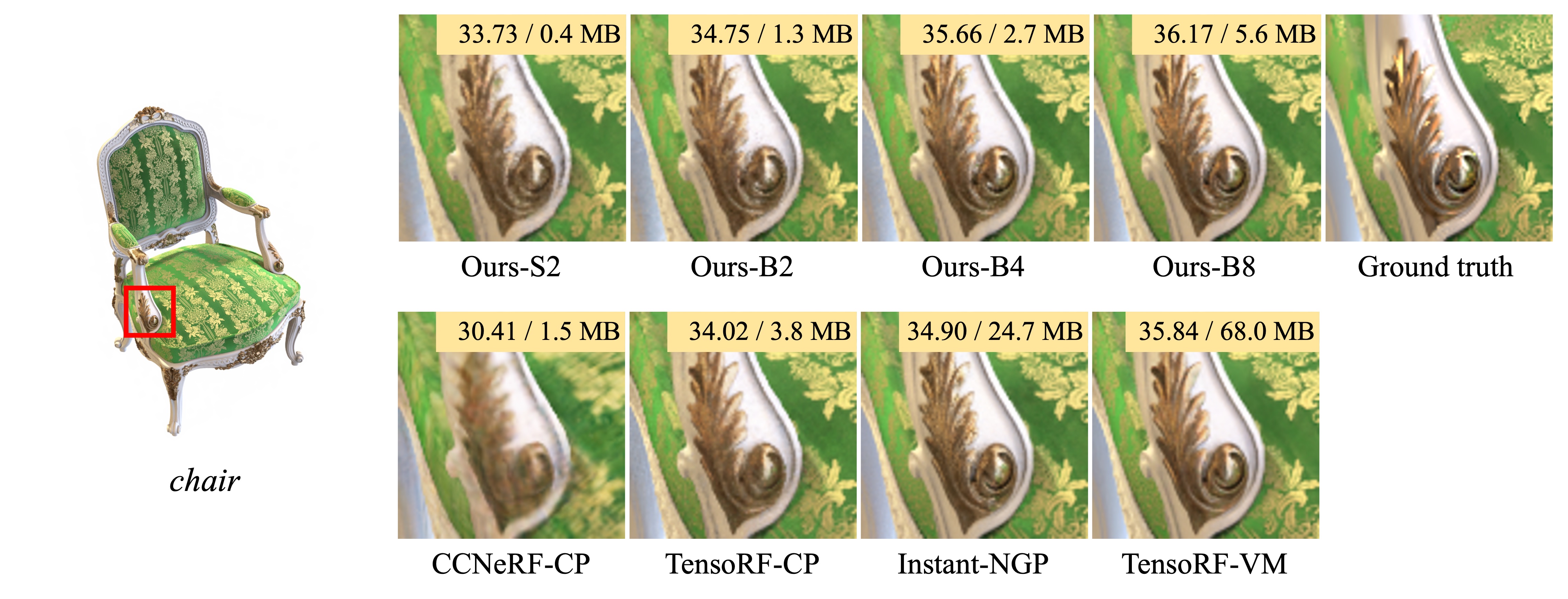
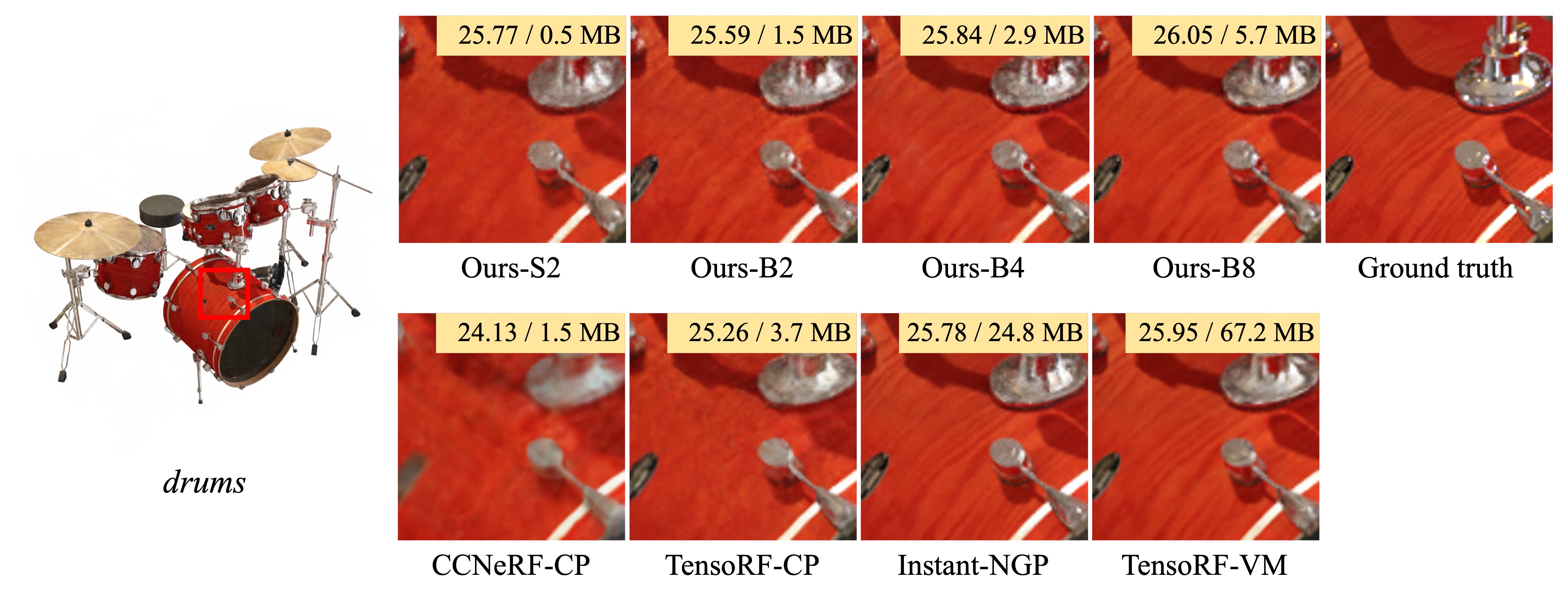

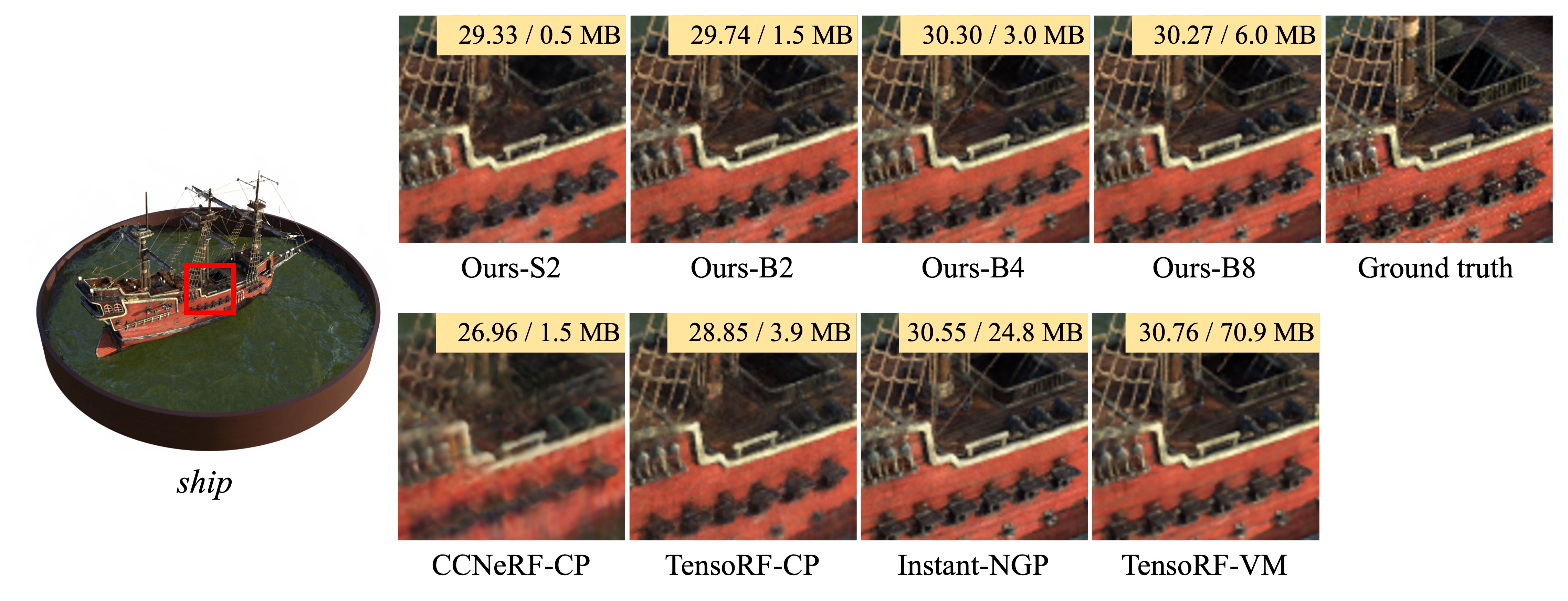


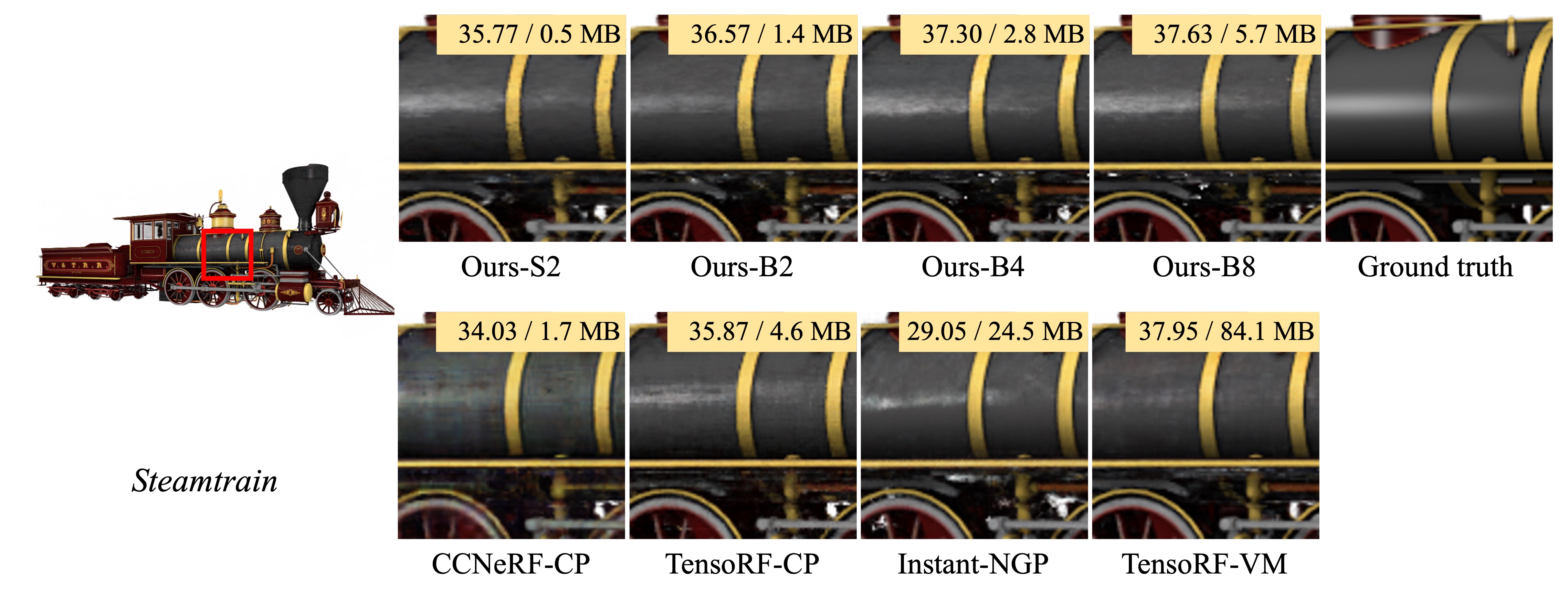
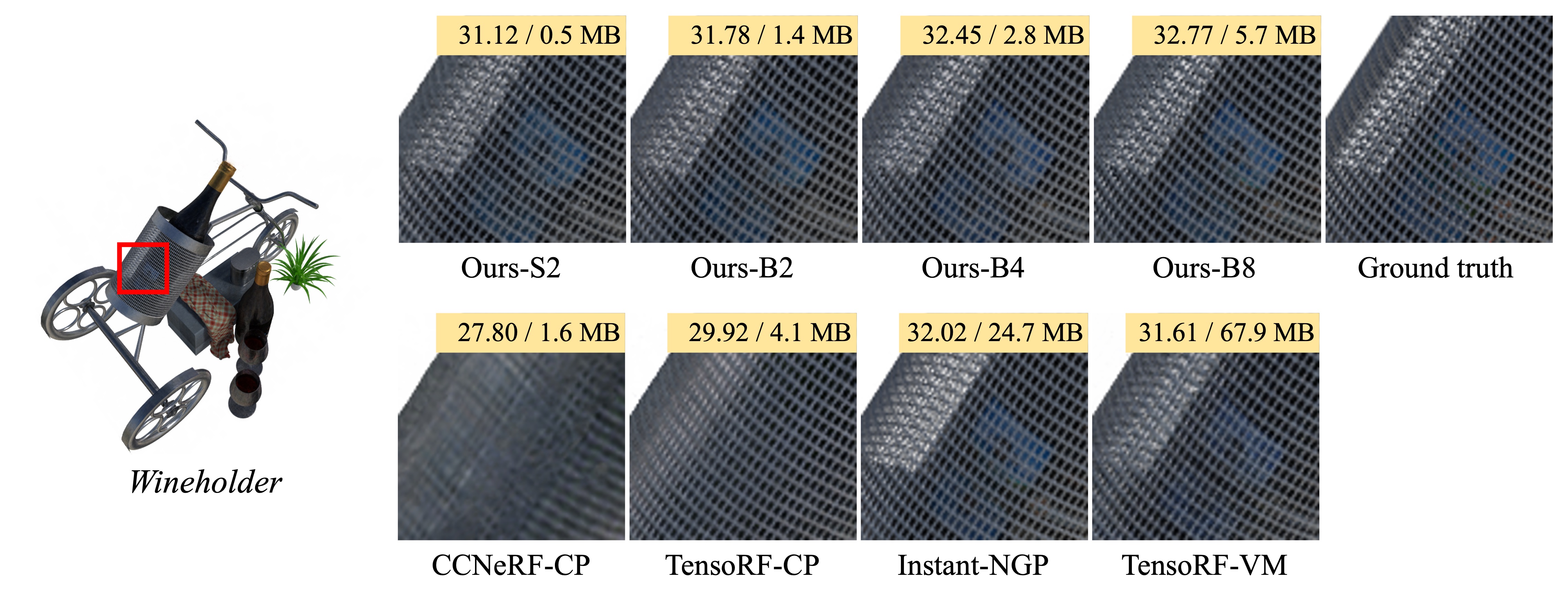
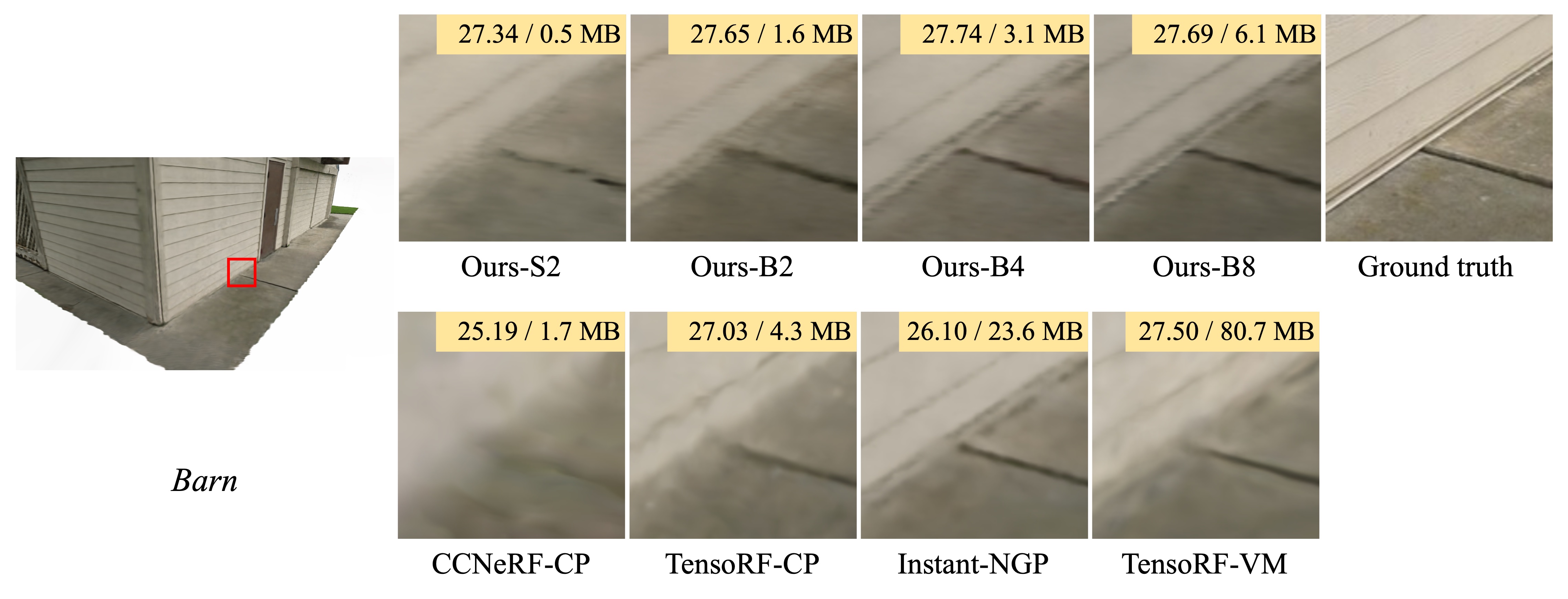


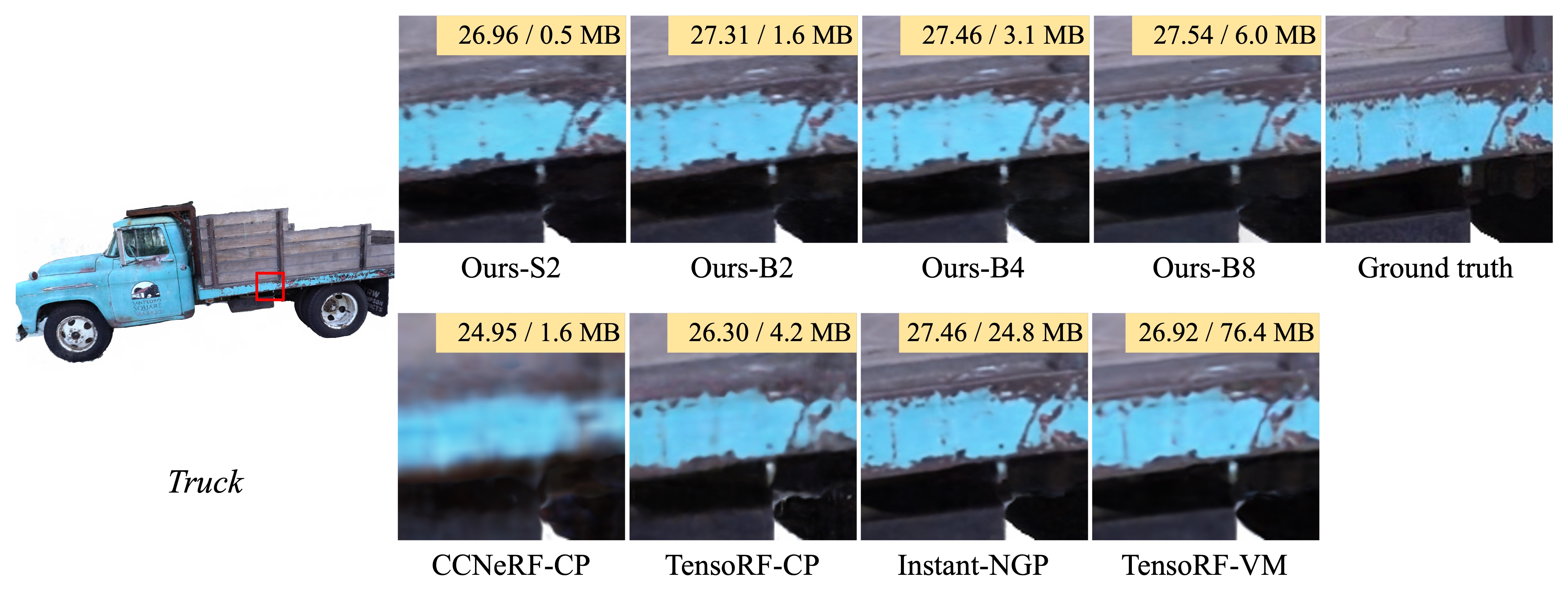
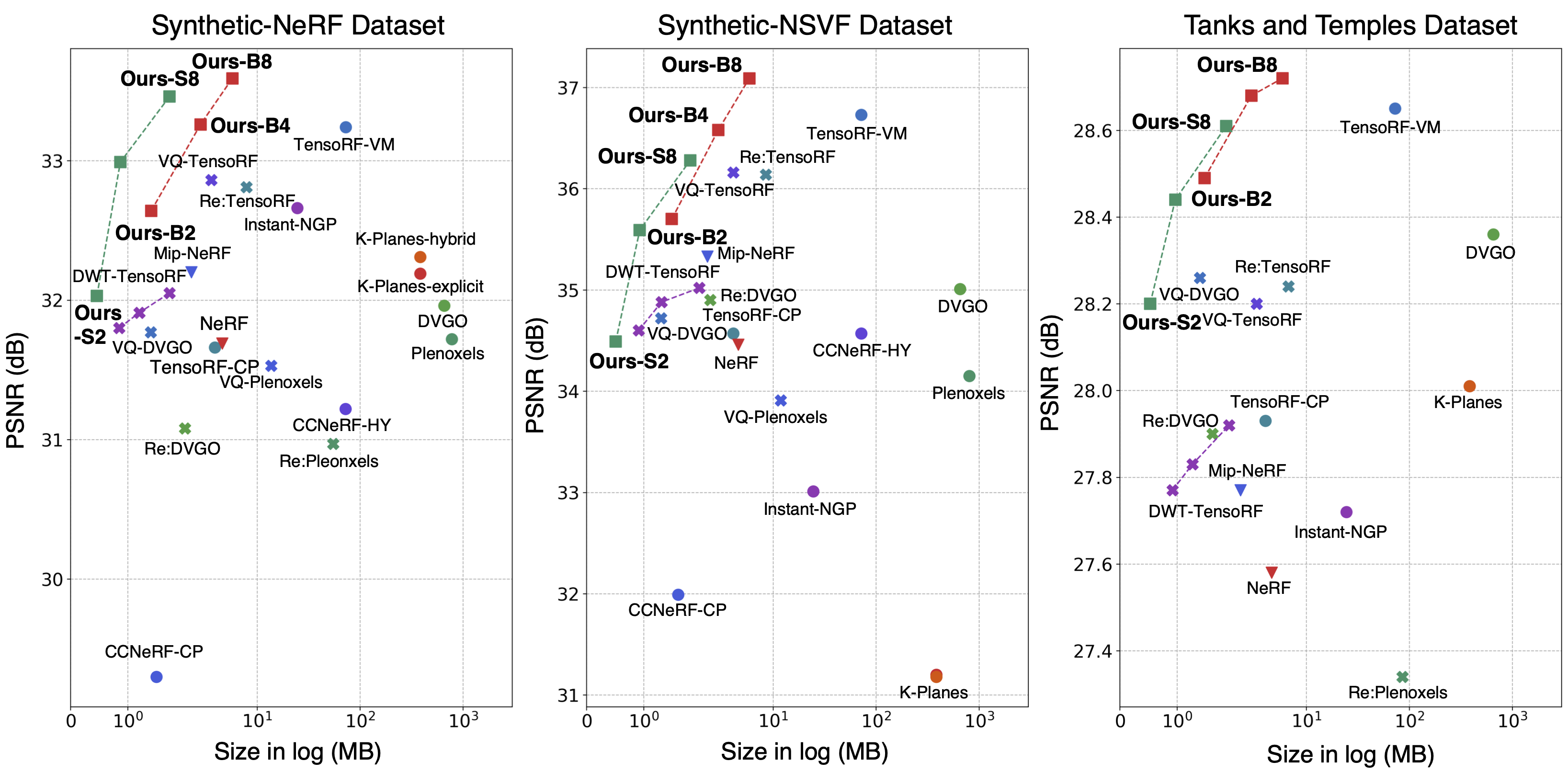
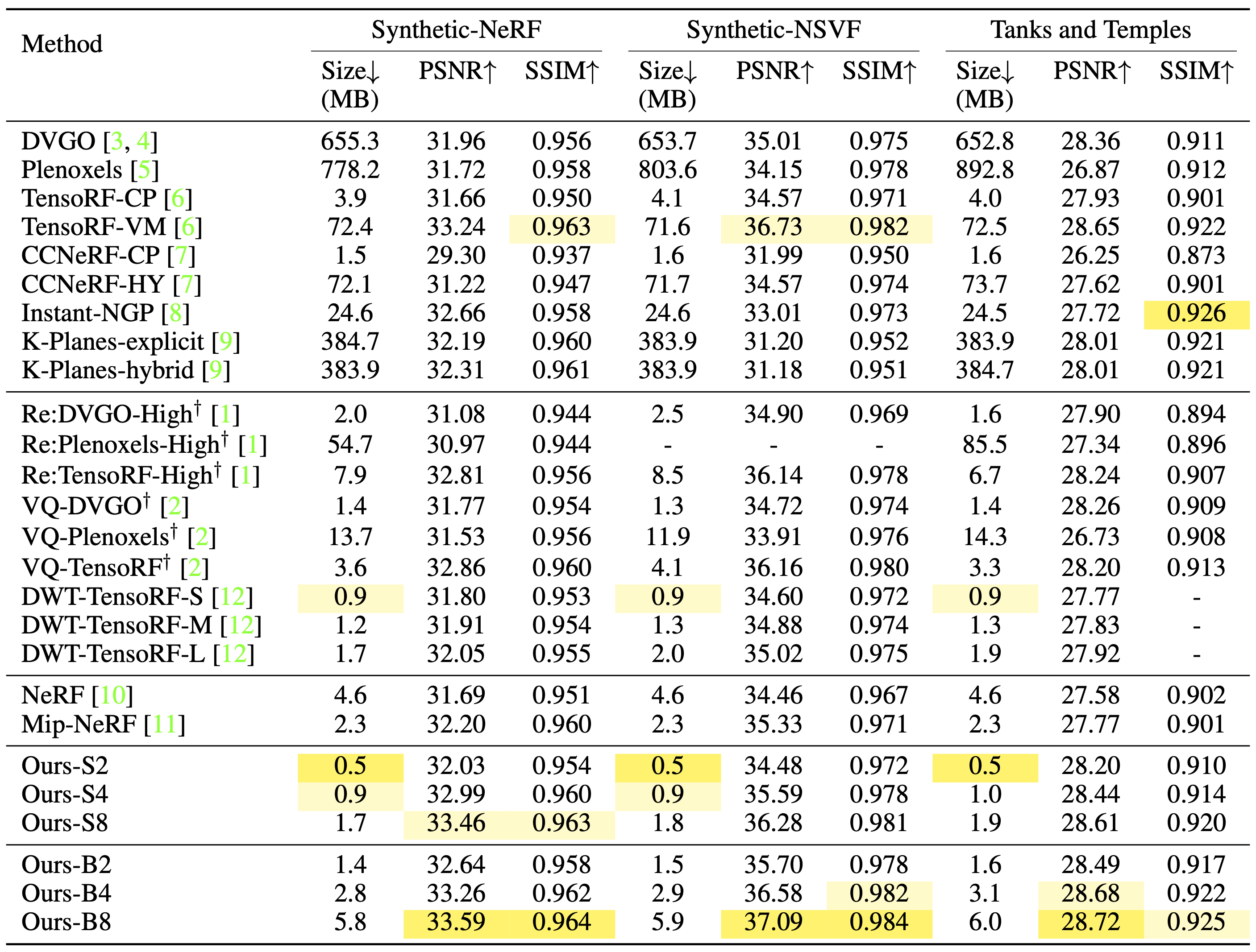
In this paper, we propose binary radiance fields (BiRF), a storage-efficient radiance field representation employing binary feature encoding that encodes local features using binary encoding parameters in a format of either +1 or -1. This binarization strategy lets us represent the feature grid with highly compact feature encoding and a dramatic reduction in storage size. Furthermore, our 2D-3D hybrid feature grid design enhances the compactness of feature encoding as the 3D grid includes main components while 2D grids capture details. In our experiments, binary radiance field representation successfully outperforms the reconstruction performance of state-of-the-art (SOTA) efficient radiance field models with lower storage allocation. In particular, our model achieves impressive results in static scene reconstruction, with a PSNR of 32.03 dB for Synthetic-NeRF scenes, 34.48 dB for Synthetic-NSVF scenes, 28.20 dB for Tanks and Temples scenes while only utilizing 0.5 MB of storage space, respectively. We hope the proposed binary radiance field representation will make radiance fields more accessible without a storage bottleneck.
@inproceedings{
shin2023binary,
title={Binary Radiance Fields},
author={Seungjoo Shin and Jaesik Park},
booktitle={Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems},
year={2023}
}